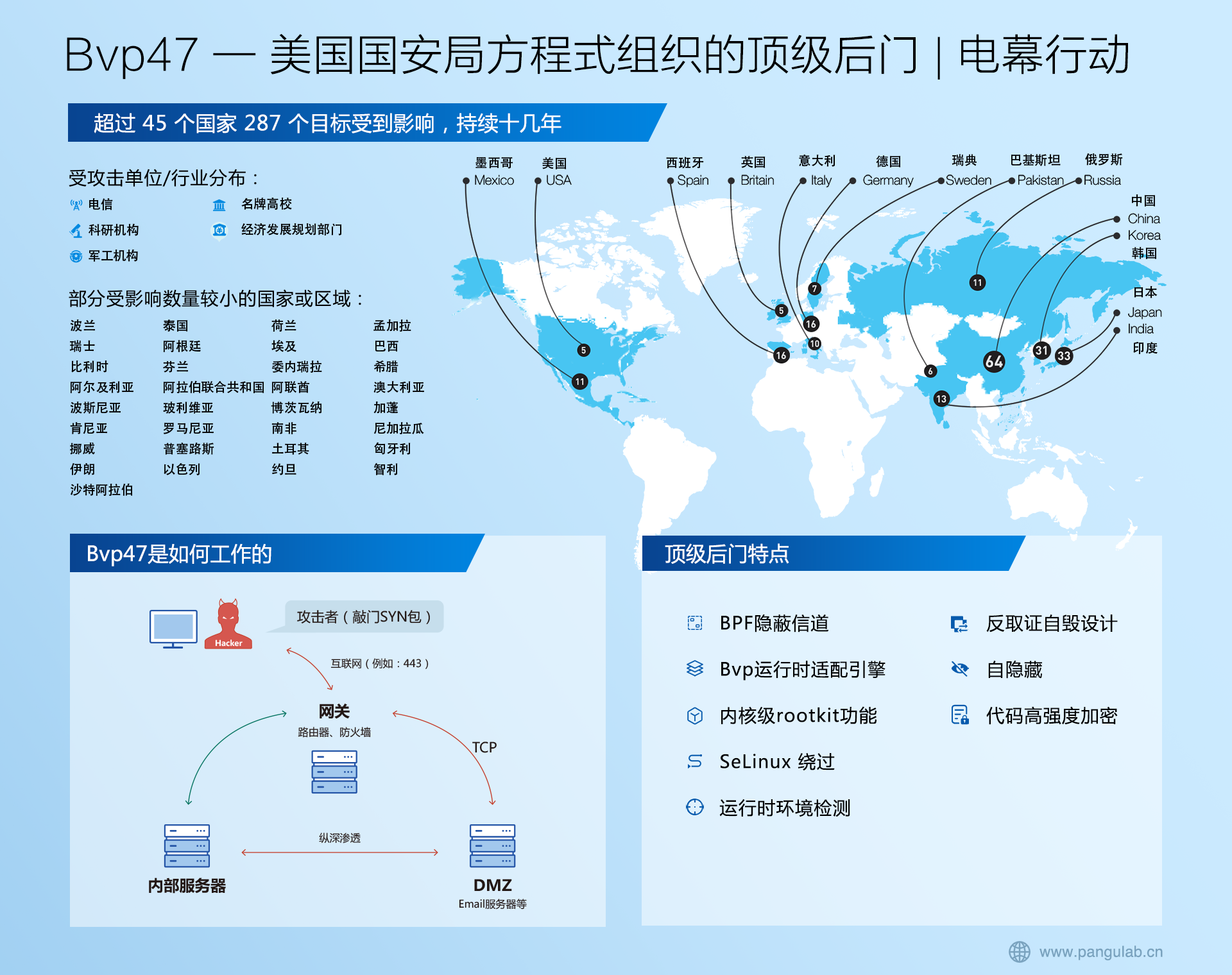
【阿旭机器学习实战】【24】信用卡用户流失预测实战
【阿旭机器学习实战】系列文章主要介绍机器学习的各种算法模型及其实战案例,欢迎点赞,关注共同学习交流。
本文针对某国外匿名化处理后的信用卡真实数据集,通过建模判断该用户是否已经流失,包括特征处理与分类模型建模评估。
目录
- 问题描述
- 1. 读取数据并分离特征与标签
- 2.特征工程
- 2.1 删除无用特征
- 2.2 将字符串特征进行编码
- 2.3 对特征数据进行归一化
- 3. 建模预测与评估
问题描述
依据某国外匿名化处理后的真实数据集,通过建模,判断该用户是否已经流失。
1. 读取数据并分离特征与标签
|
RowNumber |
CustomerId |
Surname |
CreditScore |
Geography |
Gender |
Age |
Tenure |
Balance |
NumOfProducts |
HasCrCard |
IsActiveMember |
EstimatedSalary |
|
|
0 |
1 |
15634602 |
Hargrave |
619 |
France |
Female |
42 |
2 |
0.00 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
101348.88 |
|
1 |
2 |
15647311 |
Hill |
608 |
Spain |
Female |
41 |
1 |
83807.86 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
112542.58 |
|
2 |
3 |
15619304 |
Onio |
502 |
France |
Female |
42 |
8 |
159660.80 |
3 |
1 |
0 |
113931.57 |
|
3 |
4 |
15701354 |
Boni |
699 |
France |
Female |
39 |
1 |
0.00 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
93826.63 |
|
4 |
5 |
15737888 |
Mitchell |
850 |
Spain |
Female |
43 |
2 |
125510.82 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
79084.10 |
数据说明:
RowNumber:行号
CustomerID:用户编号
Surname:用户姓名
CreditScore:信用分数
Geography:用户所在国家/地区
Gender:用户性别
Age:年龄
Tenure:当了本银行多少年用户
Balance:存贷款情况
NumOfProducts:使用产品数量
HasCrCard:是否有本行信用卡
IsActiveMember:是否活跃用户
EstimatedSalary:估计收入
Exited:是否已流失,这将作为我们的标签数据
2.特征工程
2.1 删除无用特征
|
CreditScore |
Geography |
Gender |
Age |
Tenure |
Balance |
NumOfProducts |
HasCrCard |
IsActiveMember |
EstimatedSalary |
|
|
0 |
619 |
France |
Female |
42 |
2 |
0.00 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
101348.88 |
|
1 |
608 |
Spain |
Female |
41 |
1 |
83807.86 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
112542.58 |
|
2 |
502 |
France |
Female |
42 |
8 |
159660.80 |
3 |
1 |
0 |
113931.57 |
|
3 |
699 |
France |
Female |
39 |
1 |
0.00 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
93826.63 |
|
4 |
850 |
Spain |
Female |
43 |
2 |
125510.82 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
79084.10 |
2.2 将字符串特征进行编码
|
CreditScore |
Geography |
Gender |
Age |
Tenure |
Balance |
NumOfProducts |
HasCrCard |
IsActiveMember |
EstimatedSalary |
|
|
0 |
619 |
0 |
0 |
42 |
2 |
0.00 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
101348.88 |
|
1 |
608 |
2 |
0 |
41 |
1 |
83807.86 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
112542.58 |
|
2 |
502 |
0 |
0 |
42 |
8 |
159660.80 |
3 |
1 |
0 |
113931.57 |
|
3 |
699 |
0 |
0 |
39 |
1 |
0.00 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
93826.63 |
|
4 |
850 |
2 |
0 |
43 |
2 |
125510.82 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
79084.10 |
2.3 对特征数据进行归一化
3. 建模预测与评估
结果表明该模型准确率只有76%,还有一定的优化空间。
如果内容对你有帮助,感谢点赞+关注哦!
欢迎关注我的公众号:
阿旭算法与机器学习,共同学习交流。
更多干货内容持续更新中…