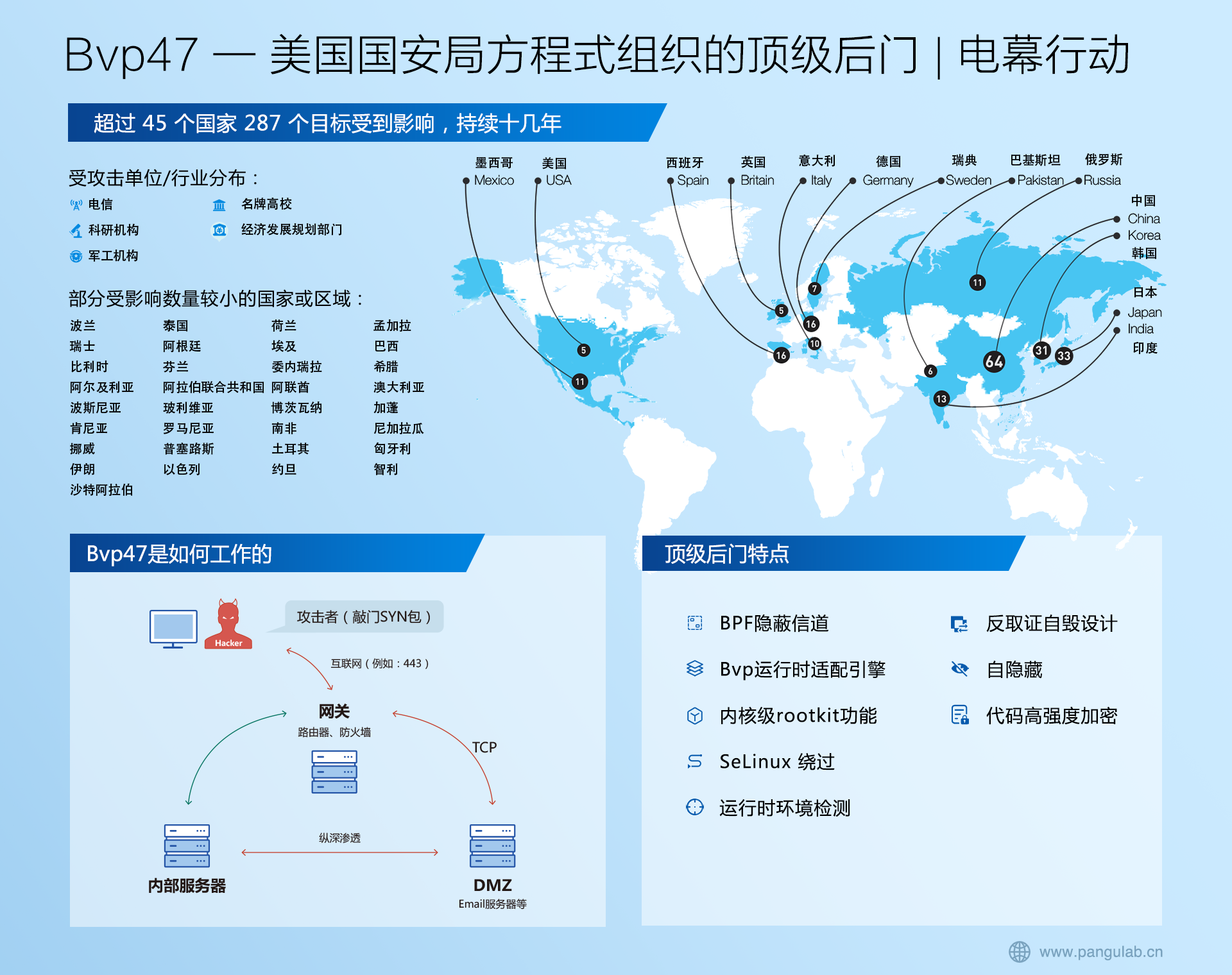
JavaScript数组遍历的方式
发布时间:2022-11-01 00:26:23 342 相关标签: # javascript# css# java# java
文章目录
- 1、 for循环
- 2、forEach函数
- 3、map函数
- 4、filter函数
- 5、some和every函数
1、 for循环
for循环是最原始的循环方法,如下代码:
const arr = [1, 23, 4, 5, 6];
for (let index = 0; index < arr.length; index++) {
const element = arr[index];
console.log(element)
}
2、forEach函数
forEach通过传入回调函数来实现遍历,代码如下:
const arr = [1, 23, 4, 5, 6];
arr.forEach((element,index)=>{
console.log(element,index)
})
但是,forEach是ES5新增的方法,可能不兼容低版本的浏览器,只能通过polyfill来完成兼容:
// forEach()函数兼容性处理
Array.prototype.forEach = Array.prototype.forEach ||
function (callback,) {
for (let index = 0, length = this.length; index < length; index++) {
if (typeof callback === "function"
&& Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(this, index)) {
callback.call(context, this[index], index, this);
}
}
};
在线应该多数的浏览器都应该支持ES5了,所以forEach的兼容性可以不用担心了。
3、map函数
map函数,在遍历数组中,对数组的每一个元素做处理,得到新的元素,并且返回一个新数组,map不会修改原数组。
const newArr = arr.map((ele) => ele * 2);
console.log('原数组', arr);//原数组 [ 1, 23, 4, 5, 6 ]
console.log('新数组', newArr);//新数组 [ 2, 46, 8, 10, 12 ]
需要注意的是,map函数遍历数组,需要return一个值,否则会返回undefined。比如:
const newArr = arr.map((ele) => {
ele * 2
});
console.log('新数组', newArr);// 新数组 [ undefined, undefined, undefined, undefined, undefined ]
map函数的兼容写法:
// map()函数兼容性处理
Array.prototype.map = Array.prototype.map ||
function (callback,) {
var arr = [];
if (typeof callback === "function") {
for (var k = 0, length = this.length; k < length; k++) {
if (typeof callback === "function"
&& Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(this, k)) {
arr.push(callback.call(context, this[k], k, this));
}
}
}
return arr;
};
4、filter函数
filter函数也是遍历数组,但它是从数组中筛选出符合条件的元素,最后组合成新的数组并且返回,代码如下:
const newArr = arr.filter((ele) => {
return ele % 2 === 0
})
console.log("new arr is", newArr); // new arr is [ 4, 6 ]
console.log("old arr is", arr) // old arr is [ 1, 23, 4, 5, 6 ]
filter()函数兼容性处理:
Array.prototype.filter = Array.prototype.filter ||
function (fn,) {
var arr = [];
if (typeof fn === "function") {
for (var k = 0, length = this.length; k < length; k++) {
if (typeof fn === "function"
&& Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(this, k)) {
fn.call(context, this[k], k, this) && arr.push(
this[k]);
}
}
}
return arr;
};
5、some和every函数
这个两个函数主要是判断数组是否符合我们给定的条件:
some函数是判断数组存在满足条件的元素,若存在满足条件的元素,则返回true,否则返回false:
const isGoodArr = arr.some(ele => ele === 1);
console.log("isGoodArr",isGoodArr) // isGoodArr true
every函数判断数组所有元素是否都满足条件,若满足,则返回true,否则返回false:
const isGoodArr = arr.every(ele => ele === 1);
console.log("isGoodArr",isGoodArr) //isGoodArr false
关于some和every的兼容写法:
// some()函数兼容性处理
Array.prototype.some = Array.prototype.some ||
function (fn,) {
var passed = false;
if (typeof fn === "function"
&&Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(this, k)) {
for (var k = 0, length = this.length; k < length; k++) {
if (passed === true) break; // 如果有返回值为“true”,直接跳出循环
passed = !!fn.call(context, this[k], k, this);
}
}
return passed;
};
// every()函数兼容性处理
Array.prototype.every = Array.prototype.every ||
function (fn,) {
var passed = true;
if (typeof fn === "function"
&&Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(this, k)) {
for (var k = 0, length = this.length; k < length; k++) {
if (passed === false) break; // 如果有返回值为“false”,直接跳出循环
passed = !!fn.call(context, this[k], k, this);
}
}
return passed;
};
文章来源: https://blog.51cto.com/u_12344418/5802216
特别声明:以上内容(图片及文字)均为互联网收集或者用户上传发布,本站仅提供信息存储服务!如有侵权或有涉及法律问题请联系我们。
举报