获取文件资源Properties

相关标签: # html# java# java# 信息
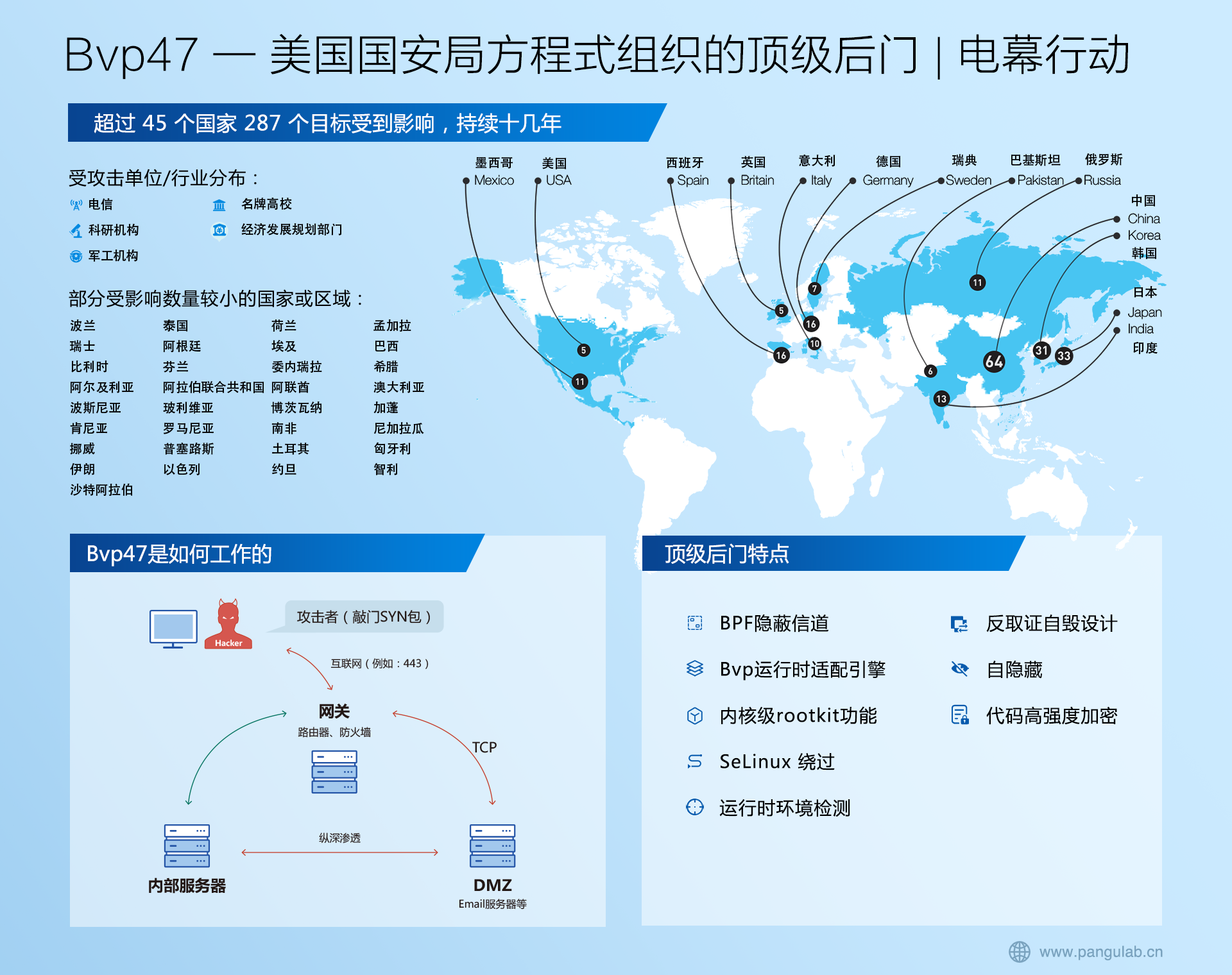
获取资源文件Properties的三种方法
工程目录截图为:
package com.gdy.getconfig;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
/*
* 处理请求为:【*.proper】
* 功能:不同方式获取不同路径下的properties配置文件信息
* 1.采用ServletContext对象获取
* 优点:任意文件,任意路径都可以获取
* 缺点:必须有web环境
* 2.采用ResourceBundle类来获取
* 优点:简单方便
* 缺点:只能拿去properties文件,2.只能拿取非web环境下的资源
* 3.采用类加载器获取
* 优点:任意文件,任意路径都可以获取。
*/
public class GservletGeProperties extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// get101();
// get102();
// get103();
get201();
get301();
}
/**
* 采用ServletContext获取文件
* 获取p1资源文件的内容
*/
protected void get101(){
//获取全局对象
ServletContext context=this.getServletContext();
//获取p1.properties文件路径[注意,有误class文件在/WEB-INF/classes下面,所有要加该路径]
String path=context.getRealPath("/WEB-INF/classes/p1.properties");
Properties pro=new Properties();
try {
pro.load(new FileReader(path));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//读取K的值
System.out.println("get101获取值为:"+pro.get("k"));
}
/**
* 采用ServletContext获取文件
* 获取p2资源文件的内容
*/
protected void get102(){
//获取全局对象
ServletContext context=this.getServletContext();
//获取p1.properties文件路径[注意,有误class文件在/WEB-INF/classes下面,所有要加该路径]
String path=context.getRealPath("/WEB-INF/classes/com/gdy/getconfig/p2.properties");
Properties pro=new Properties();
try {
pro.load(new FileReader(path));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//读取K的值
System.out.println("get102获取值为:"+pro.get("k"));
}
/**
* 采用ServletContext获取文件
* 获取p3资源文件的内容
*/
protected void get103(){
//获取全局对象
ServletContext context=this.getServletContext();
//获取p1.properties文件路径[注意,有误class文件在/WEB-INF/classes下面,所有要加该路径]
String path=context.getRealPath("/p3.properties");
Properties pro=new Properties();
try {
pro.load(new FileReader(path));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//读取K的值
System.out.println("get103获取值为:"+pro.get("k"));
}
/**
* 采用ResourceBundle
* 缺点,只能获取src目录下面的文件,不能获取web下面的文件。
* 获取p1资源文件
*/
protected void get201(){
//获取ResourceBunble获取资源文件:获取P1资源文件(由于默认路径是冲src下面开始,所有不用带“/”)
ResourceBundle rb=ResourceBundle.getBundle("p1");
//获取p2文件
ResourceBundle rbp2=ResourceBundle.getBundle("com.gdy.getconfig.p2");
//获取文件中的内容
System.out.println(rb.getString("k"));
System.out.println(rbp2.getString("k"));
}
/**
* 采用类加载器获取资源文件:获取p1资源文件
* 注意:类加载器的根目录时【/WEB-INF/class/】下面。
* 1.通过类名 GservletGeProperties.class.getClassLoader()
* 2.通过对象this.getClass().getClassLoader();
* 3。Class.forName()获取Class.forName("GservletGeProperties").getClassLoader()
*/
protected void get301(){
//更具类加载器获取指定对象流
InputStream instr=this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("p1.properties");
InputStream instrp2=this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("com/gdy/getconfig/p2.properties");
InputStream instrp3=this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("../../p3.properties");
Properties pro=new Properties();
Properties pro2=new Properties();
Properties pro3=new Properties();
try {
pro.load(instr);//加载该文件
pro2.load(instrp2);
pro3.load(instrp3);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(pro.get("k"));
System.out.println(pro2.get("k"));
System.out.println(pro3.get("k"));
}
}
web.xml配置文件为:
<servlet>
<servlet-name>getproper</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.gdy.getconfig.GservletGeProperties</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>getproper</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.proper</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
文章来源: https://blog.51cto.com/u_8406447/5769395
特别声明:以上内容(图片及文字)均为互联网收集或者用户上传发布,本站仅提供信息存储服务!如有侵权或有涉及法律问题请联系我们。
举报