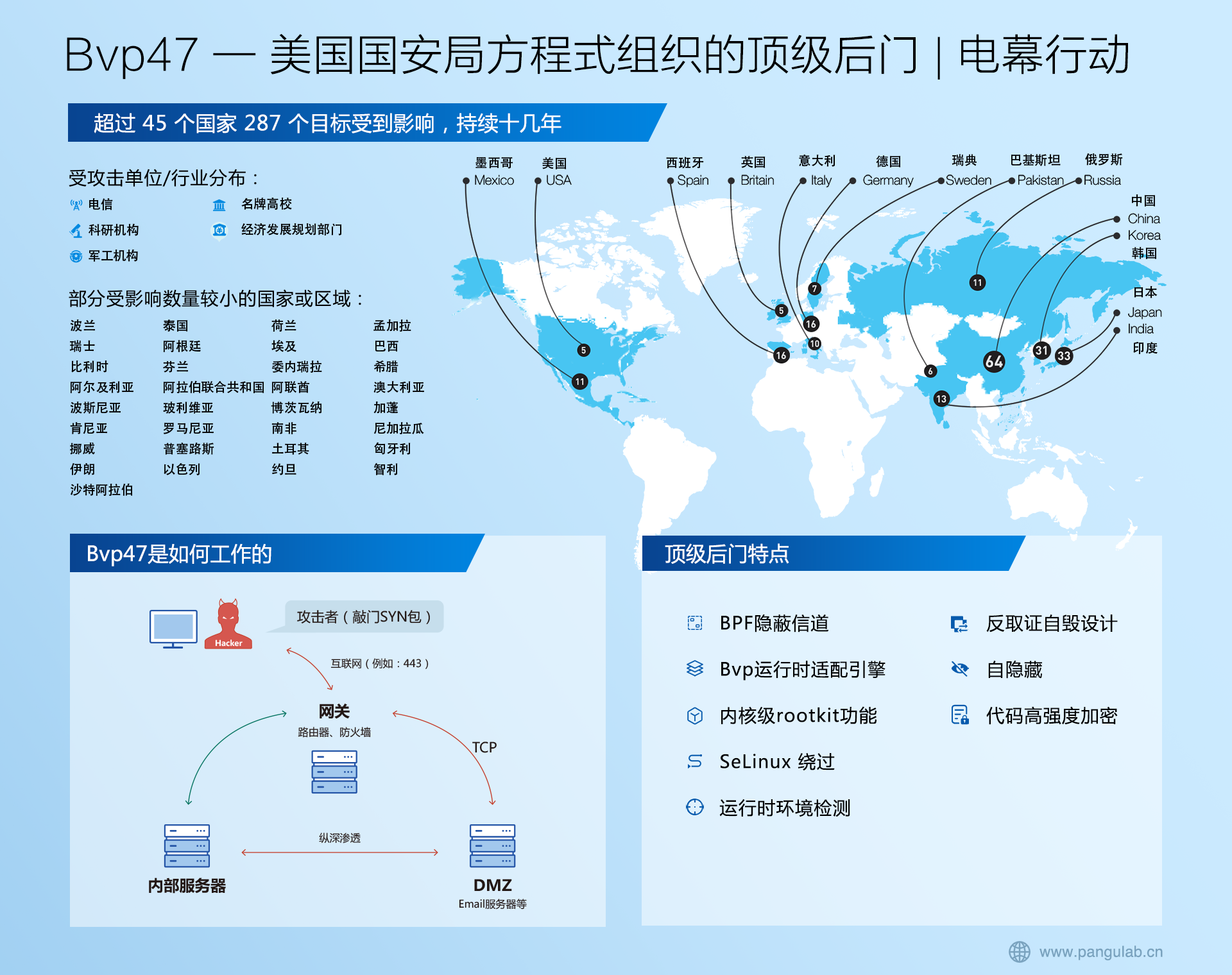
本指南将引导你完成创建负载均衡微服务的过程。
您将构建什么
您将构建一个微服务应用程序,该应用程序使用 Spring Cloud LoadBalancer 在调用另一个微服务时提供客户端负载平衡。
你需要什么
- 约15分钟
- 最喜欢的文本编辑器或 IDE
- JDK 1.8 或更高版本
- Gradle 6+ 或 Maven 3.5+
- 您也可以将代码直接导入到 IDE 中:
- Spring Tool Suite (STS) 或 IntelliJ IDEA
创建根项目
本指南将逐步介绍如何构建两个项目,其中一个项目依赖于另一个项目。因此,您需要在一个根项目下创建两个子项目。首先,在顶层创建生成配置。对于Maven,您需要一个包含子目录的列表:pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>gs-spring-cloud-loadbalancer</artifactId>
<version>0.1.0</version>
<packaging>pom</packaging>
<modules>
<module>say-hello</module>
<module>user</module>
</modules>
</project>
对于 Gradle,您需要一个包含相同目录的内容:settings.gradle
rootProject.name = 'gs-spring-cloud-loadbalancer'
include 'say-hello'
include 'user'
(可选)可以包含一个空(以帮助 IDE 识别根目录)。build.gradle
创建目录结构
在要作为根目录的目录中,创建以下子目录结构(例如,在 *nix 系统上):mkdir say-hello user
在项目的根目录中,您需要设置一个构建系统,本指南向您展示如何使用 Maven 或 Gradle。
从 Spring 初始化开始
如果您将 Maven 用于该项目,请访问Say HelloSpring Initializr以生成具有所需依赖项的新项目(Spring Web)。
以下清单显示了选择 Maven 时创建的文件:pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.0.0</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-loadbalancer-say-hello</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>spring-cloud-loadbalancer-say-hello</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<spring-boot.repackage.skip>true</spring-boot.repackage.skip>
<java.version>17</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
如果您在项目中使用 Gradle,请访问Say HelloSpring Initializr以生成具有所需依赖项的新项目(Spring Web)。
以下清单显示了选择 Gradle 时创建的文件:build.gradle
plugins {
id 'org.springframework.boot' version '3.0.0'
id 'io.spring.dependency-management' version '1.1.0'
id 'java'
}
group = 'com.example'
version = '0.0.1-SNAPSHOT'
sourceCompatibility = '17'
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web'
testImplementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test'
}
test {
useJUnitPlatform()
}
bootJar {
enabled = false
}
如果您将 Maven 用于该项目,请访问UserSpring Initializr以生成具有所需依赖项(Cloud Loadbalancer 和 Spring Reactive Web)的新项目。
以下清单显示了选择 Maven 时创建的文件:pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.0.0</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-loadbalancer-say-hello</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>spring-cloud-loadbalancer-say-hello</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<spring-boot.repackage.skip>true</spring-boot.repackage.skip>
<java.version>17</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
如果您在项目中使用 Gradle,请访问UserSpring Initializr以生成具有所需依赖项(Cloud Loadbalancer 和 Spring Reactive Web)的新项目。
以下清单显示了选择 Gradle 时创建的文件:build.gradle
plugins {
id 'org.springframework.boot' version '3.0.0'
id 'io.spring.dependency-management' version '1.1.0'
id 'java'
}
group = 'com.example'
version = '0.0.1-SNAPSHOT'
sourceCompatibility = '17'
repositories {
mavenCentral()
maven { url 'https://repo.spring.io/milestone' }
}
ext {
set('springCloudVersion', "2022.0.0")
}
dependencies {
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-webflux'
implementation 'org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-starter-loadbalancer'
testImplementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test'
testImplementation 'io.projectreactor:reactor-test'
}
dependencyManagement {
imports {
mavenBom "org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-dependencies:${springCloudVersion}"
}
}
test {
useJUnitPlatform()
}
bootJar {
enabled = false
}
手动初始化(可选)
如果要手动初始化项目而不是使用前面显示的链接,请按照以下步骤操作:
- 导航到https://start.spring.io.此服务拉入应用程序所需的所有依赖项,并为您完成大部分设置。
- 选择 Gradle 或 Maven 以及您要使用的语言。本指南假定您选择了 Java。
- 单击依赖关系,然后选择 Spring Web(对于项目)或 Cloud Loadbalancer 和 Spring Reactive Web(对于项目)。
Say HelloUser
- 单击生成。
- 下载生成的 ZIP 文件,该文件是配置了您选择的 Web 应用程序的存档。
|
如果您的 IDE 集成了 Spring Initializr,则可以从 IDE 完成此过程。
|
实施“打个招呼”服务
我们的“服务器”服务称为 。它从可在 访问的终结点返回一个随机问候语(从三个静态列表中选取)。Say Hello/greeting
在 中创建文件 。src/main/java/helloSayHelloApplication.java
下面的清单显示了以下内容:say-hello/src/main/java/hello/SayHelloApplication.java
package hello;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@SpringBootApplication
public class SayHelloApplication {
private static Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SayHelloApplication.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SayHelloApplication.class, args);
}
@GetMapping("/greeting")
public String greet() {
log.info("Access /greeting");
List greetings = Arrays.asList("Hi there", "Greetings", "Salutations");
Random rand = new Random();
int randomNum = rand.nextInt(greetings.size());
return greetings.get(randomNum);
}
@GetMapping("/")
public String home() {
log.info("Access /");
return "Hi!";
}
}
这是一个简单的 ,我们有一个用于 ,另一个用于根路径。@RestController@RequestMapping method/greeting/
我们将在本地运行此应用程序的多个实例以及客户端服务应用程序。要开始使用:
- 创建目录。
src/main/resources
- 在目录中创建一个文件。
application.yml
- 在该文件中,为 设置默认值。
server.port
(我们将指示应用程序的其他实例在其他端口上运行,以便在我们运行该实例时不会与客户端冲突)。当我们在此文件中时,我们也可以为我们的服务设置。Say Hellospring.application.name
下面的清单显示了以下内容:say-hello/src/main/resources/application.yml
spring:
application:
name: say-hello
server:
port: 8090
从客户端服务访问
我们的用户会看到该应用程序。它调用应用程序以获取问候语,然后在用户访问 和 的终结点时将该问候语发送给我们的用户。UserSay Hello/hi/hello
在“用户应用程序目录”的“下”下,添加文件:src/main/java/helloUserApplication.java
以下清单显示了user/src/main/java/hello/UserApplication.java
package hello;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.reactive.ReactorLoadBalancerExchangeFilterFunction;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.function.client.WebClient;
/**
* @author Olga Maciaszek-Sharma
*/
@SpringBootApplication
@RestController
public class UserApplication {
private final WebClient.Builder loadBalancedWebClientBuilder;
private final ReactorLoadBalancerExchangeFilterFunction lbFunction;
public UserApplication(WebClient.Builder webClientBuilder,
ReactorLoadBalancerExchangeFilterFunction lbFunction) {
this.loadBalancedWebClientBuilder = webClientBuilder;
this.lbFunction = lbFunction;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(UserApplication.class, args);
}
@RequestMapping("/hi")
public Mono hi(@RequestParam(value = "name", defaultValue = "Mary") String name) {
return loadBalancedWebClientBuilder.build().get().uri("http://say-hello/greeting")
.retrieve().bodyToMono(String.class)
.map(greeting -> String.format("%s, %s!", greeting, name));
}
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public Mono hello(@RequestParam(value = "name", defaultValue = "John") String name) {
return WebClient.builder()
.filter(lbFunction)
.build().get().uri("http://say-hello/greeting")
.retrieve().bodyToMono(String.class)
.map(greeting -> String.format("%s, %s!", greeting, name));
}
}
我们还需要一个类来设置负载均衡实例:@ConfigurationWebClient.Builder
下面的清单显示了以下内容:user/src/main/java/hello/WebClientConfig.java
package hello;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalanced;
import org.springframework.cloud.loadbalancer.annotation.LoadBalancerClient;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.function.client.WebClient;
@Configuration
@LoadBalancerClient(name = "say-hello", configuration = SayHelloConfiguration.class)
public class WebClientConfig {
@LoadBalanced
@Bean
WebClient.Builder webClientBuilder() {
return WebClient.builder();
}
}
该配置提供了一个实例,当有人命中 .一旦端点被命中,我们使用此构建器创建一个实例,该实例向服务的 URL 发出 HTTP 请求,并将结果作为 .@LoadBalanced WebClient.BuilderhiUserApplication.javahiWebClientGETSay HelloString
在 中,我们还添加了一个执行相同操作的终结点。但是,我们没有使用注释,而是使用负载均衡器交换筛选器函数 (),我们通过使用该方法将其传递给以编程方式生成的实例。UserApplication.java/hello@LoadBalanced@AutowiredlbFunctionfilter()WebClient
|
|
尽管我们为两个终端节点设置的负载均衡实例略有不同,但两者的最终行为完全相同。Spring Cloud LoadBalancer用于选择服务的适当实例。WebClientSay Hello
|
将 and 属性添加到 或 :spring.application.nameserver.portsrc/main/resources/application.propertiessrc/main/resources/application.yml
以下清单显示了user/src/main/resources/application.yml
spring:
application:
name: user
server:
port: 8888
跨服务器实例的负载平衡
现在我们可以访问或在用户服务上看到友好的问候语:/hihello
$ curl http://localhost:8888/hi
Greetings, Mary!
$ curl http://localhost:8888/hi?name=Orontes
Salutations, Orontes!
在 中,我们使用注释传递负载均衡器的自定义配置:WebClientConfig.java@LoadBalancerClient
@LoadBalancerClient(name = "say-hello", configuration = SayHelloConfiguration.class)
这意味着,每当联系名为的服务时,Spring Cloud Balancer 都会使用 .say-helloSayHelloConfiguration.java
下面的清单显示了以下内容:user/src/main/java/hello/SayHelloConfiguration.java
package hello;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import reactor.core.publisher.Flux;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.DefaultServiceInstance;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.ServiceInstance;
import org.springframework.cloud.loadbalancer.core.ServiceInstanceListSupplier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
/**
* @author Olga Maciaszek-Sharma
*/
public class SayHelloConfiguration {
@Bean
@Primary
ServiceInstanceListSupplier serviceInstanceListSupplier() {
return new DemoServiceInstanceListSuppler("say-hello");
}
}
class DemoServiceInstanceListSuppler implements ServiceInstanceListSupplier {
private final String serviceId;
DemoServiceInstanceListSuppler(String serviceId) {
this.serviceId = serviceId;
}
@Override
public String getServiceId() {
return serviceId;
}
@Override
public Flux<List> get() {
return Flux.just(Arrays
.asList(new DefaultServiceInstance(serviceId + "1", serviceId, "localhost", 8090, false),
new DefaultServiceInstance(serviceId + "2", serviceId, "localhost", 9092, false),
new DefaultServiceInstance(serviceId + "3", serviceId, "localhost", 9999, false)));
}
}
在该类中,我们提供了一个包含三个硬编码实例的自定义,Spring Cloud LoadBalancer 在调用服务时会从中进行选择。ServiceInstanceListSupplierSay Hello
|
|
添加此步骤是为了说明如何将自己的自定义配置传递给 Spring 云负载均衡器。但是,您无需使用注释并为负载均衡器创建自己的配置。最典型的方法是将Spring Cloud LoadBalancer与服务发现一起使用。如果您的类路径上有,则默认的 Spring 云负载均衡器配置使用它来检查服务实例。因此,您只能从已启动并正在运行的实例中进行选择。您可以学习如何使用它@LoadBalancerClientDiscoveryClientServiceDiscovery指导.
|
我们还添加一个默认文件和.application.ymlserver.portspring.application.name
下面的清单显示了以下内容:user/src/main/resources/application.yml
spring:
application:
name: user
server:
port: 8888
测试负载均衡器
以下清单显示了如何使用 Gradle 运行该服务:Say Hello
以下清单显示了如何使用 Maven 运行该服务:Say Hello
您可以在端口 9092 和 9999 上运行其他实例 要使用 Gradle,请运行以下命令:
$ SERVER_PORT=9092 ./gradlew bootRun
若要使用 Maven 执行此操作,请运行以下命令:
$ SERVER_PORT=9999 mvn spring-boot:run
然后,您可以启动该服务。为此,请访问并监视服务实例。Userlocalhost:8888/hiSay Hello
您对服务的请求应导致调用以轮循机制方式分布在正在运行的实例中:UserSay Hello
2016-03-09 21:15:28.915 INFO 90046 --- [nio-8090-exec-7] hello.SayHelloApplication : Access /greeting
总结
祝贺!您刚刚开发了一个 Spring 负载均衡器应用程序!