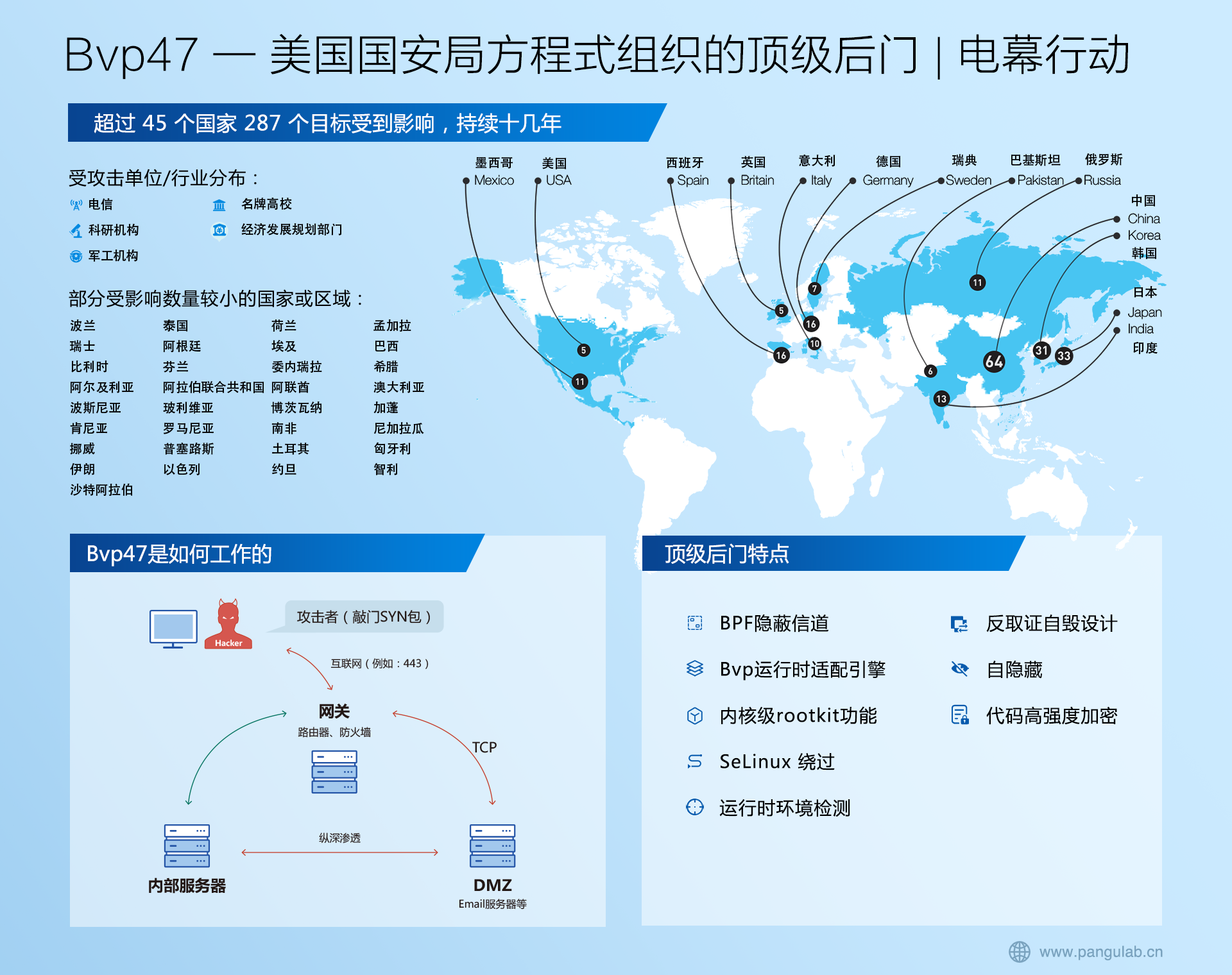
SpringBoot——异常报告器解析
异常报告器类介绍
接口规范
@FunctionalInterface
public interface SpringBootExceptionReporter {
/**
* Report a startup failure to the user.
* @param failure the source failure
* @return {@code true} if the failure was reported or {@code false} if default
* reporting should occur.
*/
boolean reportException(Throwable failure);
}
SpringBootExceptionReporter初始化情况
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
......
//初始化构造一个SpringBootExceptionReporter集合
Collection exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
try {
...
//给exceptionReporters集合填充具体的对象
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
...
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
...
return context;
}
通过SpringFactoriesLoader加载
private Collection getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class type, Class[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
ClassLoader classLoader = getClassLoader();
// Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates
Set names = new LinkedHashSet<>(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
// 也是通过SpringFactoriesLoader技术来加载,见下图,默认就一个,这边实例化会调用其构造函数
List instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);
return instances;
}
# Error Reporters
org.springframework.boot.SpringBootExceptionReporter=\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalyzers
SpringBoot通过SPI技术为SpringBootExceptionReporter接口指定了唯一的实现FailureAnalyzers
final class FailureAnalyzers implements SpringBootExceptionReporter {
private final ClassLoader classLoader;
private final List analyzers;
FailureAnalyzers(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ClassLoader classLoader) {
Assert.notNull(context, "Context must not be null");
//设置类加载器
this.classLoader = (classLoader != null) ? classLoader : context.getClassLoader();
//获取容器中FailureAnalyzer实例对象并排序
this.analyzers = loadFailureAnalyzers(this.classLoader);
prepareFailureAnalyzers(this.analyzers, context);
}
private List loadFailureAnalyzers(ClassLoader classLoader) {
List analyzerNames = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(FailureAnalyzer.class, classLoader);
List analyzers = new ArrayList<>();
for (String analyzerName : analyzerNames) {
try {
Constructor constructor = ClassUtils.forName(analyzerName, classLoader).getDeclaredConstructor();
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(constructor);
analyzers.add((FailureAnalyzer) constructor.newInstance());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
logger.trace("Failed to load " + analyzerName, ex);
}
}
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(analyzers);
return analyzers;
}
private void prepareFailureAnalyzers(List analyzers, ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
for (FailureAnalyzer analyzer : analyzers) {
prepareAnalyzer(context, analyzer);
}
}
private void prepareAnalyzer(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, FailureAnalyzer analyzer) {
if (analyzer instanceof BeanFactoryAware) {
((BeanFactoryAware) analyzer).setBeanFactory(context.getBeanFactory());
}
if (analyzer instanceof EnvironmentAware) {
((EnvironmentAware) analyzer).setEnvironment(context.getEnvironment());
}
}
}
再看List
@FunctionalInterface
public interface FailureAnalyzer {
/**
* Returns an analysis of the given {@code failure}, or {@code null} if no analysis
* was possible.
* @param failure the failure
* @return the analysis or {@code null}
*/
//对异常进行分析返回FailureAnalysis
FailureAnalysis analyze(Throwable failure);
}
public class FailureAnalysis {
//错误描述
private final String description;
//引起错误的动作
private final String action;
//错误本身
private final Throwable cause;
}
下面我们看下FailureAnalyzers实现的SpringBootExceptionReporter的异常报告方法
@Override
public boolean reportException(Throwable failure) {
FailureAnalysis analysis = analyze(failure, this.analyzers);
return report(analysis, this.classLoader);
}
private FailureAnalysis analyze(Throwable failure, List analyzers) {
for (FailureAnalyzer analyzer : analyzers) {
try {
// 依次遍历每个analyzer分析,有结果就返回,这边走到AbstractFailureAnalyzer的analyze方法
FailureAnalysis analysis = analyzer.analyze(failure);
if (analysis != null) {
return analysis;
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("FailureAnalyzer " + analyzer + " failed", ex);
}
}
}
return null;
}
AbstractFailureAnalyzer实现了FailureAnalyzer接口
public abstract class AbstractFailureAnalyzer implements FailureAnalyzer {
@Override
public FailureAnalysis analyze(Throwable failure) {
// 会先走到这里
T cause = findCause(failure, getCauseType());
if (cause != null) {
// 找到子类感兴趣的异常后,调用具体实现类的分析方法
return analyze(failure, cause);
}
return null;
}
protected abstract FailureAnalysis analyze(Throwable rootFailure, T cause);
// 这个就是解析我的泛型参数,表明我对哪个异常感兴趣
protected Class getCauseType() {
return (Class) ResolvableType.forClass(AbstractFailureAnalyzer.class, getClass()).resolveGeneric();
}
protected final E findCause(Throwable failure, Class type) {
// 依次遍历异常堆栈,如果有对当前异常感兴趣,就返回,否则返回null
while (failure != null) {
if (type.isInstance(failure)) {
return (E) failure;
}
failure = failure.getCause();
}
return null;
}
}
再来看看report(analysis, this.classLoader)方法
// 分析出结果之后,调用report方法之后报告异常
private boolean report(FailureAnalysis analysis, ClassLoader classLoader) {
// FailureAnalysisReporter这个实现类只有一个,是LoggingFailureAnalysisReporter
List reporters = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactories(FailureAnalysisReporter.class,
classLoader);
if (analysis == null || reporters.isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
for (FailureAnalysisReporter reporter : reporters) {
// 输出异常报告
reporter.report(analysis);
}
return true;
}
public final class LoggingFailureAnalysisReporter implements FailureAnalysisReporter {
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(LoggingFailureAnalysisReporter.class);
@Override
public void report(FailureAnalysis failureAnalysis) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Application failed to start due to an exception", failureAnalysis.getCause());
}
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error(buildMessage(failureAnalysis));
}
}
private String buildMessage(FailureAnalysis failureAnalysis) {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
builder.append(String.format("%n%n"));
builder.append(String.format("***************************%n"));
builder.append(String.format("APPLICATION FAILED TO START%n"));
builder.append(String.format("***************************%n%n"));
builder.append(String.format("Description:%n%n"));
builder.append(String.format("%s%n", failureAnalysis.getDescription()));
if (StringUtils.hasText(failureAnalysis.getAction())) {
builder.append(String.format("%nAction:%n%n"));
builder.append(String.format("%s%n", failureAnalysis.getAction()));
}
return builder.toString();
}
}
SpringBoot异常处理流程
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
......
Collection exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
......
try {
......
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
......
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
//对启动过程中的失败进行处理
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
......
return context;
}
点进去handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners)
private void handleRunFailure(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception,
Collection exceptionReporters, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners) {
try {
try {
handleExitCode(context, exception);
if (listeners != null) {
listeners.failed(context, exception);
}
}
finally {
reportFailure(exceptionReporters, exception);
if (context != null) {
context.close();
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
logger.warn("Unable to close ApplicationContext", ex);
}
ReflectionUtils.rethrowRuntimeException(exception);
}
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners)逻辑

handleExitCode(context, exception)
private void handleExitCode(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception) {
// 获取框架内对这个异常定义的exitCode,代表退出状态码,为0代表正常退出,不为0标识异常退出
int exitCode = getExitCodeFromException(context, exception);
if (exitCode != 0) {
if (context != null) {
// 发布一个ExitCodeEvent事件
context.publishEvent(new ExitCodeEvent(context, exitCode));
}
SpringBootExceptionHandler handler = getSpringBootExceptionHandler();
if (handler != null) {
//记录exitCode
handler.registerExitCode(exitCode);
}
}
}
listeners.failed(context, exception)
- 发布ApplicationFailedEvent事件
public void failed(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception) {
for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners) {
callFailedListener(listener, context, exception);
}
}
private void callFailedListener(SpringApplicationRunListener listener, ConfigurableApplicationContext context,
Throwable exception) {
try {
listener.failed(context, exception);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (exception == null) {
ReflectionUtils.rethrowRuntimeException(ex);
}
if (this.log.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.log.error("Error handling failed", ex);
}
else {
String message = ex.getMessage();
message = (message != null) ? message : "no error message";
this.log.warn("Error handling failed (" + message + ")");
}
}
}
public class EventPublishingRunListener implements SpringApplicationRunListener, Ordered {
@Override
public void failed(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception) {
ApplicationFailedEvent event = new ApplicationFailedEvent(this.application, this.args, context, exception);
if (context != null && context.isActive()) {
// Listeners have been registered to the application context so we should
// use it at this point if we can
context.publishEvent(event);
}
else {
// An inactive context may not have a multicaster so we use our multicaster to
// call all of the context's listeners instead
if (context instanceof AbstractApplicationContext) {
for (ApplicationListener listener : ((AbstractApplicationContext) context)
.getApplicationListeners()) {
this.initialMulticaster.addApplicationListener(listener);
}
}
this.initialMulticaster.setErrorHandler(new LoggingErrorHandler());
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(event);
}
}
}
reportFailure(exceptionReporters, exception)
- SpringBootExceptionReporter实现类调用reportException方法
- 成功处理的话,记录已处理异常
private void reportFailure(Collection exceptionReporters, Throwable failure) {
try {
for (SpringBootExceptionReporter reporter : exceptionReporters) {
if (reporter.reportException(failure)) {
registerLoggedException(failure);
return;
}
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// Continue with normal handling of the original failure
}
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Application run failed", failure);
registerLoggedException(failure);
}
}
context.close()
- 更改应用上下文状态
- 销毁单例bean
- 将beanFactory置为空
- 关闭web容器(web环境)
- 移除shutdownHook
public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext extends DefaultResourceLoader
implements ConfigurableApplicationContext {
@Override
public void close() {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
doClose();
// If we registered a JVM shutdown hook, we don't need it anymore now:
// We've already explicitly closed the context.
if (this.shutdownHook != null) {
try {
// 移除钩子方法
Runtime.getRuntime().removeShutdownHook(this.shutdownHook);
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
// ignore - VM is already shutting down
}
}
}
}
protected void doClose() {
// Check whether an actual close attempt is necessary...
if (this.active.get() && this.closed.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Closing " + this);
}
LiveBeansView.unregisterApplicationContext(this);
try {
// Publish shutdown event.
// 发布容器关闭事件
publishEvent(new ContextClosedEvent(this));
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
logger.warn("Exception thrown from ApplicationListener handling ContextClosedEvent", ex);
}
// Stop all Lifecycle beans, to avoid delays during individual destruction.
if (this.lifecycleProcessor != null) {
try {
this.lifecycleProcessor.onClose();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
logger.warn("Exception thrown from LifecycleProcessor on context close", ex);
}
}
// Destroy all cached singletons in the context's BeanFactory.
// 销毁所有的单例bean
destroyBeans();
// Close the state of this context itself.
// 关闭容器
closeBeanFactory();
// Let subclasses do some final clean-up if they wish...
// 调用子类的重写方法,关闭web服务器
onClose();
// Reset local application listeners to pre-refresh state.
if (this.earlyApplicationListeners != null) {
this.applicationListeners.clear();
this.applicationListeners.addAll(this.earlyApplicationListeners);
}
// Switch to inactive.
this.active.set(false);
}
}
}
ReflectionUtils.rethrowRuntimeException(exception)
- 重新抛出异常
public static void rethrowRuntimeException(Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) ex;
}
if (ex instanceof Error) {
throw (Error) ex;
}
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(ex);
}
shutdownHook介绍
- 作用:JVM退出时执行的业务逻辑
- 添加:Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook()
- 移除:Runtime.getRuntime().removeShutdownHook(this.shutdownHook)
背景
在开发中,遇到这种情况,多个线程同时工作,突然一个线程遇到了fetal的错误,需要立即终止程序,等人工排查解决了问题之后重新启动。但是这样会有一个问题,程序终止时,其他线程可能正在进行重要操作,比如发一个message到另一个模块,并更新数据库状态。突然终止,可能会让这个操作只完成一半,从而导致数据不一致。
解决方案是:参考数据库Transaction原子性的概念,将这一系列重要操作看作一个整体,要么全部完成,要么全部不完成。为方便表述,我们把这一系列重要操作记为操作X。
当程序即将退出时,查看当前是否有操作X在执行中,如果有,等待其完成然后退出。且期间不再接受新的操作X。如果操作X执行之间过长,终止并回滚所有状态。
如果没有,则可以立即退出。
在程序退出的时候,做一些Check,保证已经开始的操作X的原子性,这里就用到了Runtime.ShutdownHook。
什么是Shutdown Hook
Shutdown hook是一个initialized but unstarted thread。当JVM开始执行shutdown sequence时,会并发运行所有registered Shutdown Hook。这时,在Shutdown Hook这个线程里定义的操作便会开始执行。
需要注意的是,在Shutdown Hook里执行的操作应当是不太耗时的。因为在用户注销或者操作系统关机导致的JVM shutdown的例子中,系统只会预留有限的时间给未完成的工作,超时之后还是会强制关闭。
什么时候会调用Shutdown Hook
程序正常停止
- Reach the end of program
- System.exit
程序异常退出
- NPE
- OutOfMemory
受到外界影响停止
- Ctrl+C
- 用户注销或者关机
如何使用Shutdown Hook
调用java.lang.Runtime这个类的addShutdownHook(Thread hook)方法即可注册一个Shutdown Hook,然后在Thread中定义需要在system exit时进行的操作。如下:
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(() -> System.out.println("Do something in Shutdown Hook")));
测试例子
- 首先,注册了一个Shutdown Hook。
- 然后,系统Sleep 3秒,模拟进行某些操作。
- 然后,调用一个空的List,抛出异常,准备结束程序。
- 在程序将要结束的时候,执行Shutdown Hook中的内容。
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// register shutdown hook
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(() -> System.out.println("Do something in Shutdown Hook")));
// sleep for some time
try {
for (int i=0; i<3; i++) {
System.out.println("Count: " + i + "...");
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(1000);
}
List nullList = new ArrayList<>();
System.out.println("Trying to print null list's first element: " + nullList.get(0).toString());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Ready to exit.");
System.exit(0);
}
结果如下:
Count: 0...
Count: 1...
Count: 2...
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException: Index: 0, Size: 0
at java.util.ArrayList.rangeCheck(ArrayList.java:653)
at java.util.ArrayList.get(ArrayList.java:429)
at HookTest.main(HookTest.java:18)
Do something in Shutdown Hook
Process finished with exit code 1
需要注意的点
- 当System.exit之后,当Shutdown Hook开始执行时,其他的线程还是会继续执行。
- 应当保证Shutdown Hook的线程安全。
- 在使用多个Shutdown Hook时一定要特别小心,保证其调用的服务不会被其他Hook影响。否则会出现当前Hook所依赖的服务被另外一个Hook终止了的情况。
参考: https://my.oschina.net/liwanghong/blog/3167733
https://www.cnblogs.com/maxstack/p/9112711.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/tracer-dhy/p/10041643.html