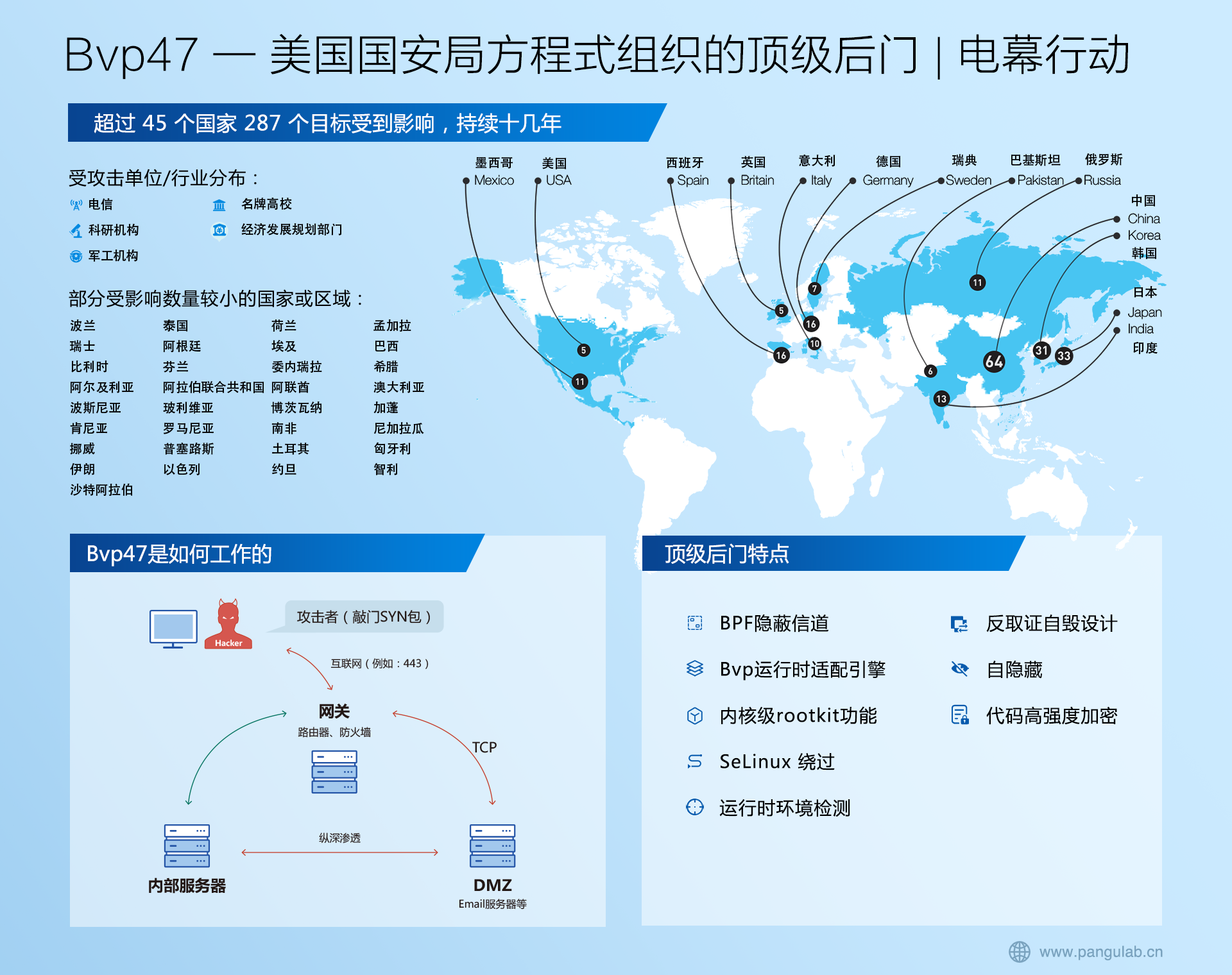
Spring5 AOP——AbstractAutoProxyCreator横切逻辑织入目标Bean中
Spring AOP的总体流程
- 1、注册解析AOP的服务
- 2、解析和加载横切逻辑
- 3、将横切逻辑织入目标Bean中
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator继承体系图

AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator既实现了SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 又实现了BeanFactoryAware。就可以对容器做一些事情。
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator 实现了Order接口,所以先于普通的BeanPostProcessor注册,并对普通BeanPostProcessor也能起作用。
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator 是InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor,会在Bean被创建之前,在resolveBeforeInstantiation中被调用。
Spring Aop主要是通过AbstractAutoProxyCreator实现的BeanPostProcessor、InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor以及SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口里面的后置处理器方法,来介入到Spring IOC容器的Bean的实例化以及初始化的过程中对Bean进行AOP的处理的。
所以AbstractAutoProxyCreator类里面的实现的容器级别的后置处理器方法便是介入分析的点:
- 横切逻辑的加载主要是在AbstractAutoProxyCreator类中的postProcessBeforeInstantiation方法中,该方法是在Bean的实例化之前被调用的。
- 横切逻辑织入目标Bean中主要是在AbstractAutoProxyCreator类中的postProcessAfterInitialization方法中,该方法是在Bean的实例化之后被调用的。
public abstract class AbstractAutoProxyCreator extends ProxyProcessorSupport
implements SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor, BeanFactoryAware {
//当 Bean 被循环引用, 并且被暴露了,
// 则会通过 getEarlyBeanReference 来创建代理类;
// 通过判断 earlyProxyReferences 中
// 是否存在 beanName 来决定是否需要对 target 进行动态代理
private final Map<Object, Object> earlyProxyReferences = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16);
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) {
if (bean != null) {
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
//当 Bean 被循环引用, 并且被暴露了,
// 则会通过 getEarlyBeanReference 来创建代理类;
// 通过判断 earlyProxyReferences 中
// 是否存在 beanName 来决定是否需要对 target 进行动态代理
if (this.earlyProxyReferences.remove(cacheKey) != bean) {
//该方法将会返回代理类
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}
}
AbstractAutoProxyCreator的postProcessAfterInitialization方法是在AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory类中的createBean方法中的创建Bean实例方法doCreateBean方法中的的对bean进行初始化方法initializeBean方法中被最终调用的。
initializeBean
public abstract class AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory extends AbstractBeanFactory
implements AutowireCapableBeanFactory {
protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
// 1.激活Aware方法
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
}
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
// 2.在初始化前应用BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法,允许对bean实例进行包装
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
// 3.调用初始化方法
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
// 4.在初始化后应用BeanPostProcessor的postProcessAfterInitialization方法,允许对bean实例进行包装
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
// 5.返回wrappedBean
return wrappedBean;
}
@Override
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
// 1.遍历所有注册的BeanPostProcessor实现类,调用postProcessAfterInitialization方法
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
// 2.在bean初始化后,调用postProcessAfterInitialization方法
Object current = processor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName);
if (current == null) {
// 3.如果返回null,则不会调用后续的BeanPostProcessors
return result;
}
result = current;
}
return result;
}
}